services offered
BONE DENSITOMETRY
Bone Densitometry, or DEXA scan, is a quick and painless procedure that measures bone loss. This is a common exam for the lower back and hips as these areas are most often affected by osteoporosis. This exam can help determine your risk of fracture. If you have metallic hardware in your back or hips, your forearm may be used for measurement as well.
Bone mineral is measured with what we call a T-score; this number shows the amount of bone you have compared to other adults of the same age and gender. Scores above -1 are normal. A score between -1 to -2.5 can show the first stage of bone loss known as osteopenia. A score below -2.5 is defined as osteoporosis.
BREAST MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging, commonly known as MRI, creates hundreds of imagines using magnetic fields and radio waves. A Breast MRI is a highly sensitive, non-invasive procedure that examines the breast.
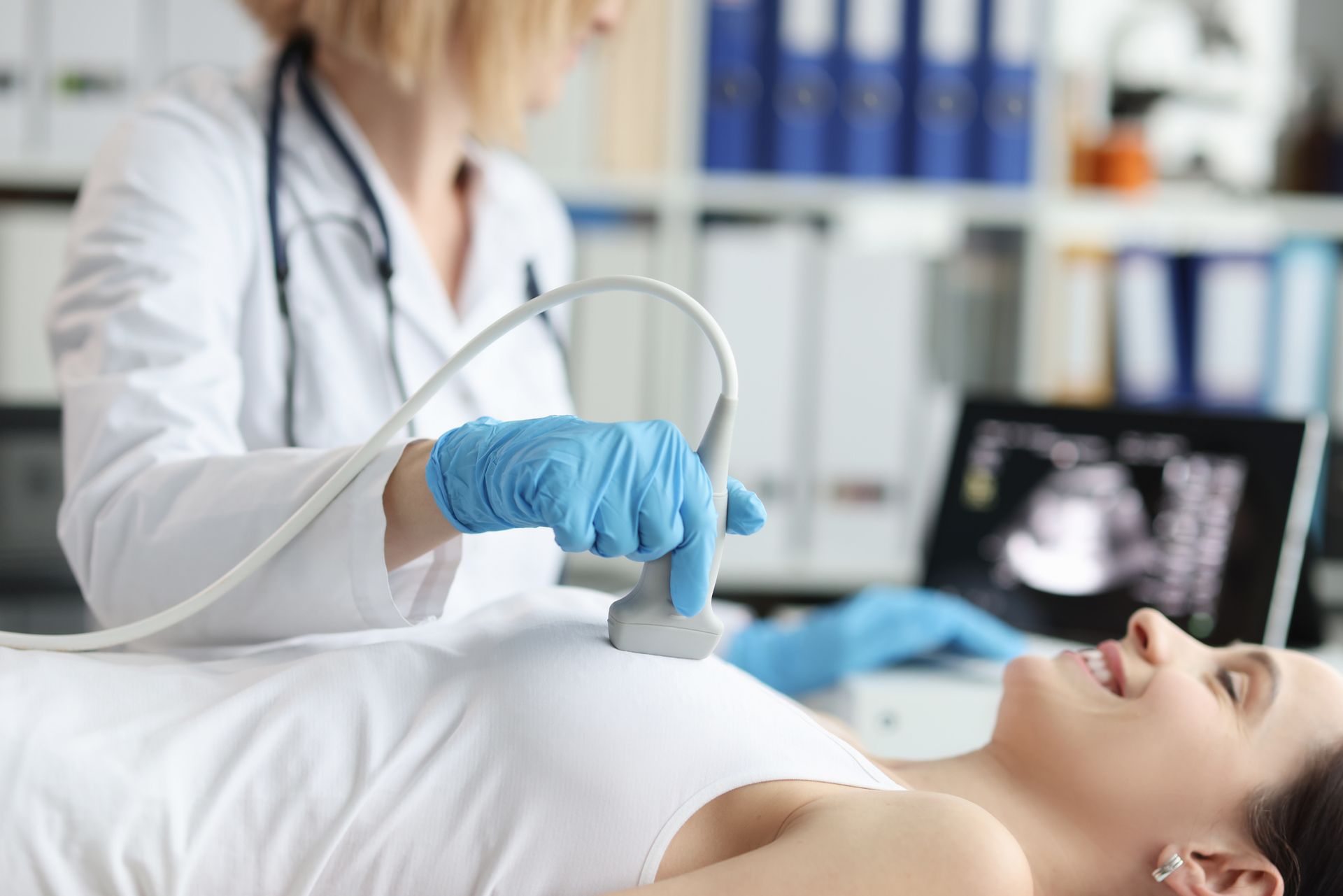
breast ultrasound
Information obtained from a breast physical examination alone may be incomplete. Breast ultrasonography, when used in conjunction with a physical exam and/or mammography, can identify cysts, tumors, abscessed, lymph nodes, and very dense breast tissue. In some cases, a tissue sample (biopsy) of a suspicious area is required to make a specific diagnosis. If this is needed, ultrasonography can be used to guide the needle biopsy without the need for surgery. Aspiration of breast cysts is commonly performed using ultrasound guidance.
Cardiac calcium scoring uses CT (Computed Tomography) scan to create images of the heart in a non-invasive manner. Calcium scoring is a screening exam performed on the CT scanner to determine if a patient has coronary artery disease (CAD). Many times, patients have no symptoms of this disease. Measuring the amount of calcium built up in the arteries, calcium scoring determines the presence of CAD. The extent of a patient’s CAD if found is also a result of this study.
CALCIUM SCORING CT
CARDIAC CTA
A coronary computed tomography angiogram, or cardiac CTA, is preformed on a CT scanner and uses “contrast” or dye to procedure images of the heart and blood vessels. The procedure is minimally invasive and can help diagnosis cardiac disorders by producing high-quality detailed 3D images. Cardiac CTA can be used to rule out stenosis, assess plaque buildup and visualize blood vessels.
A contrast-enhanced mammogram (CEM) is just like a regular mammogram, but with an additional step. Before receiving a mammogram, you get an IV injection of iodine-based dye. The dye highlights abnormal blood vessels and hyperactive tissues that can happen when cancers develop. Contrast-enhanced mammograms can evaluate the functional state of breast tissues much like breast MRI can. This enables us to detect breast cancer early.
CONTRAST-ENHANCED MAMMOGRAM
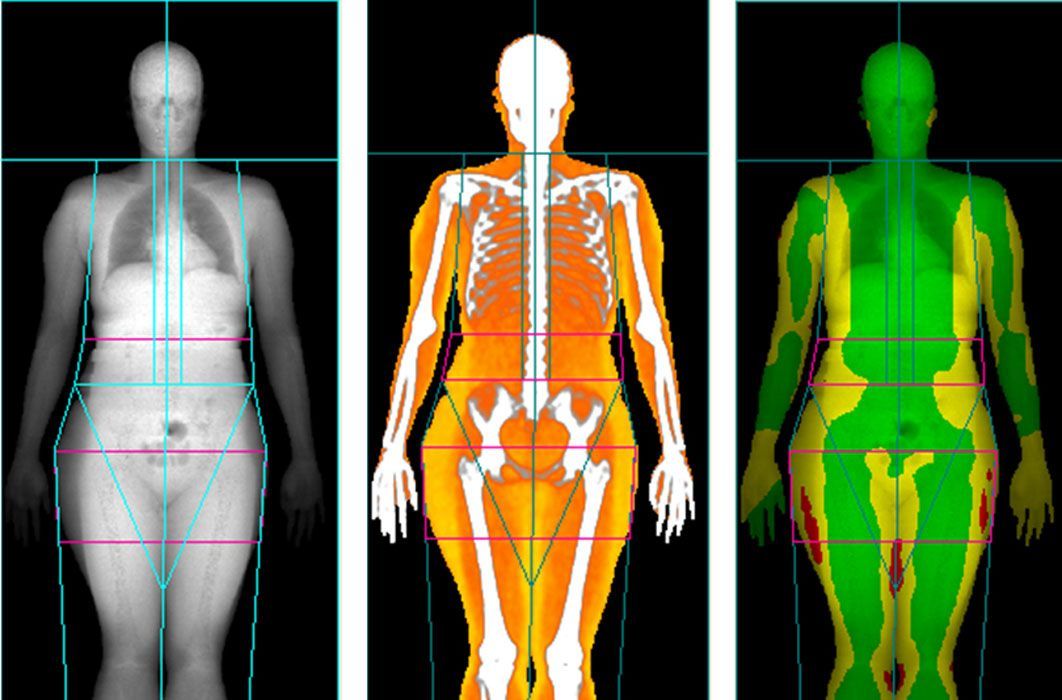
CoreScan is an FDA-approved technology that measures wellness. Specifically, it measures VAT (visceral adipose tissue) and bone density using a bone mineral density scan. VAT is fat that surrounds abdominal organs. Excess VAT levels are linked to obesity and have been shown to increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes, heart disease, hypertension and other diseases.
We offer this screening as part of our commitment to community health and wellness, a top priority for our imaging network.
CORESCAN
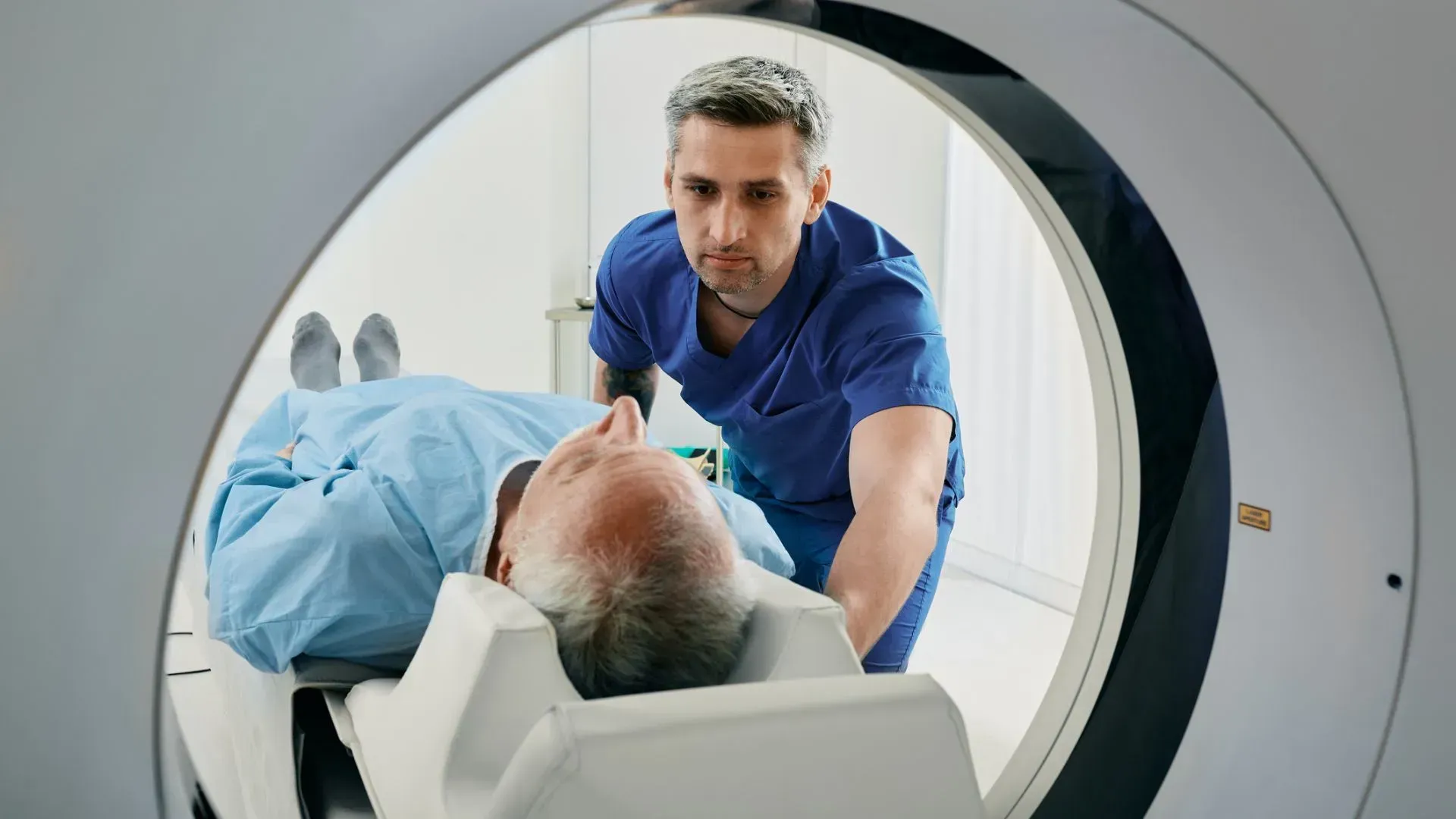
The CT, or computed tomography, scanner operated by rotating an x-ray tube around your body while measuring the constantly changing absorption of the x-ray beam by different tissues in your body. The information is then fed into a computer which produces a reconstructed image of a thin cross section or "slice" of the body. Because the scanner is very sensitive, small differences in absorption of the beam by various body tissues are recorded sharper and clearer than even the best x-ray.
CT SCAN
A low-dose lung CT screen produces images of the lungs for analysis of potential lung cancer. A screening is just a study to test for the presence of a disease without symptoms in high-risk patients. This exam uses CT (Computed Tomography) to produce high-quality images with a minimal dose of radiation.
LOW DOSE LUNG SCREENING CT
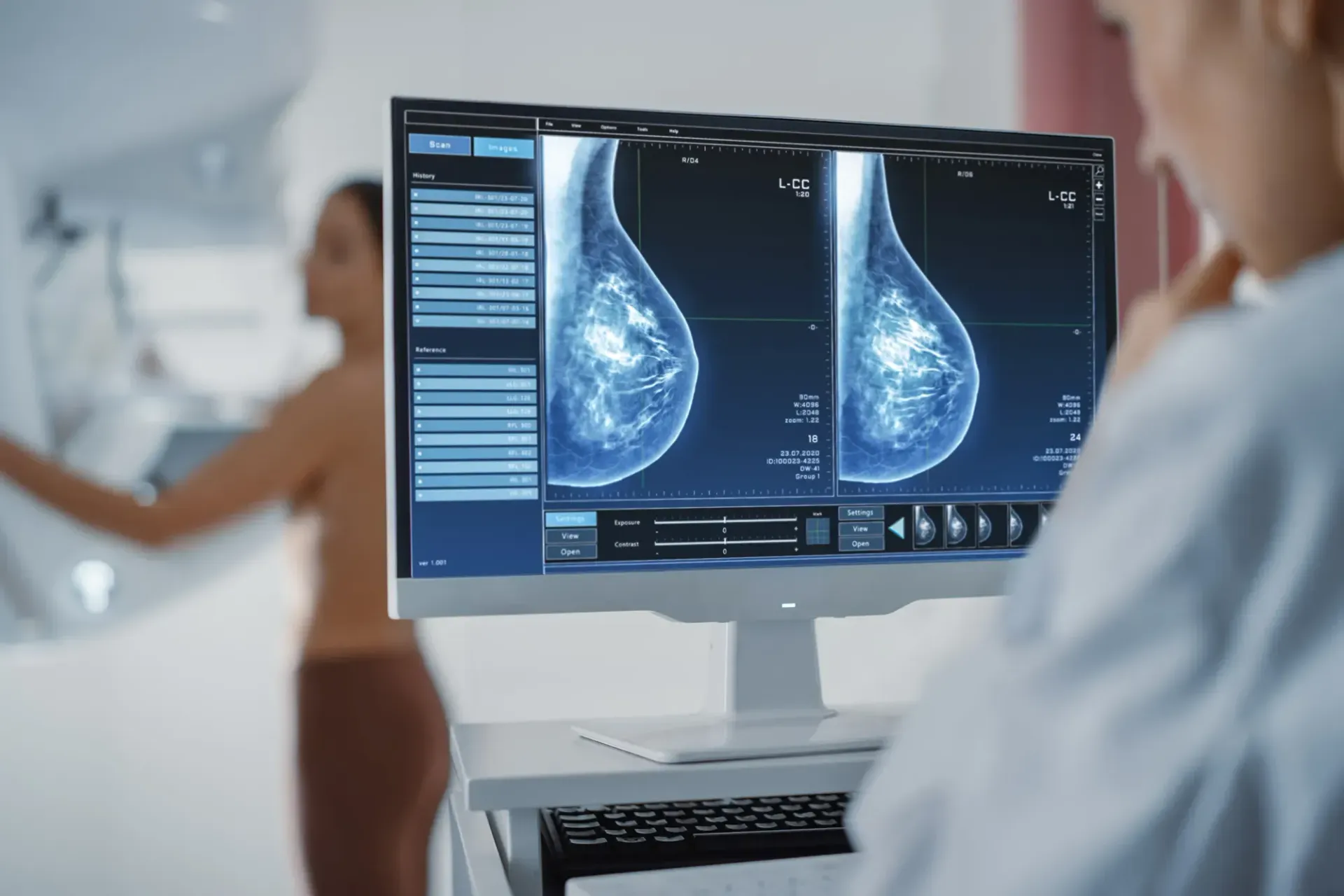
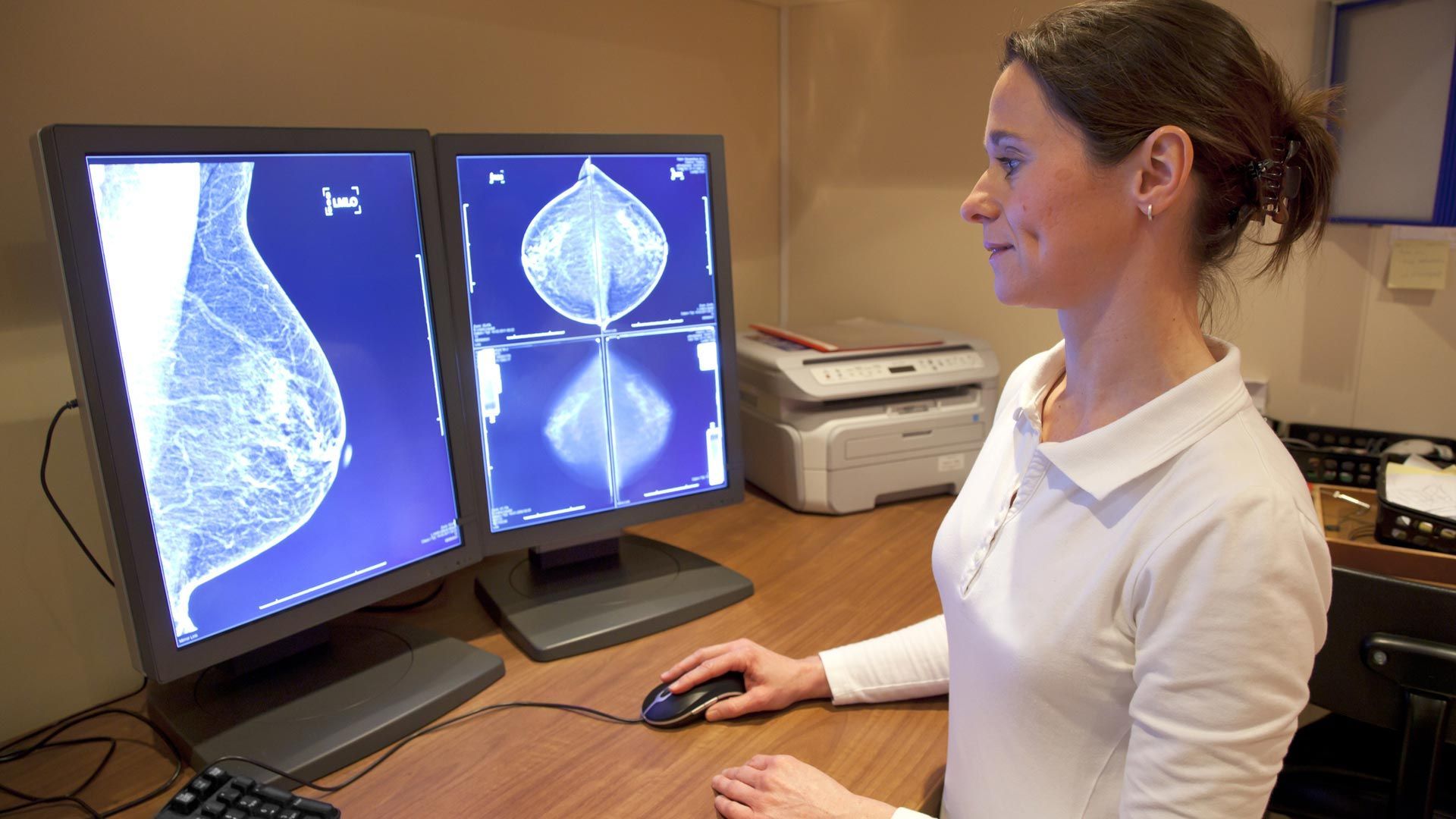
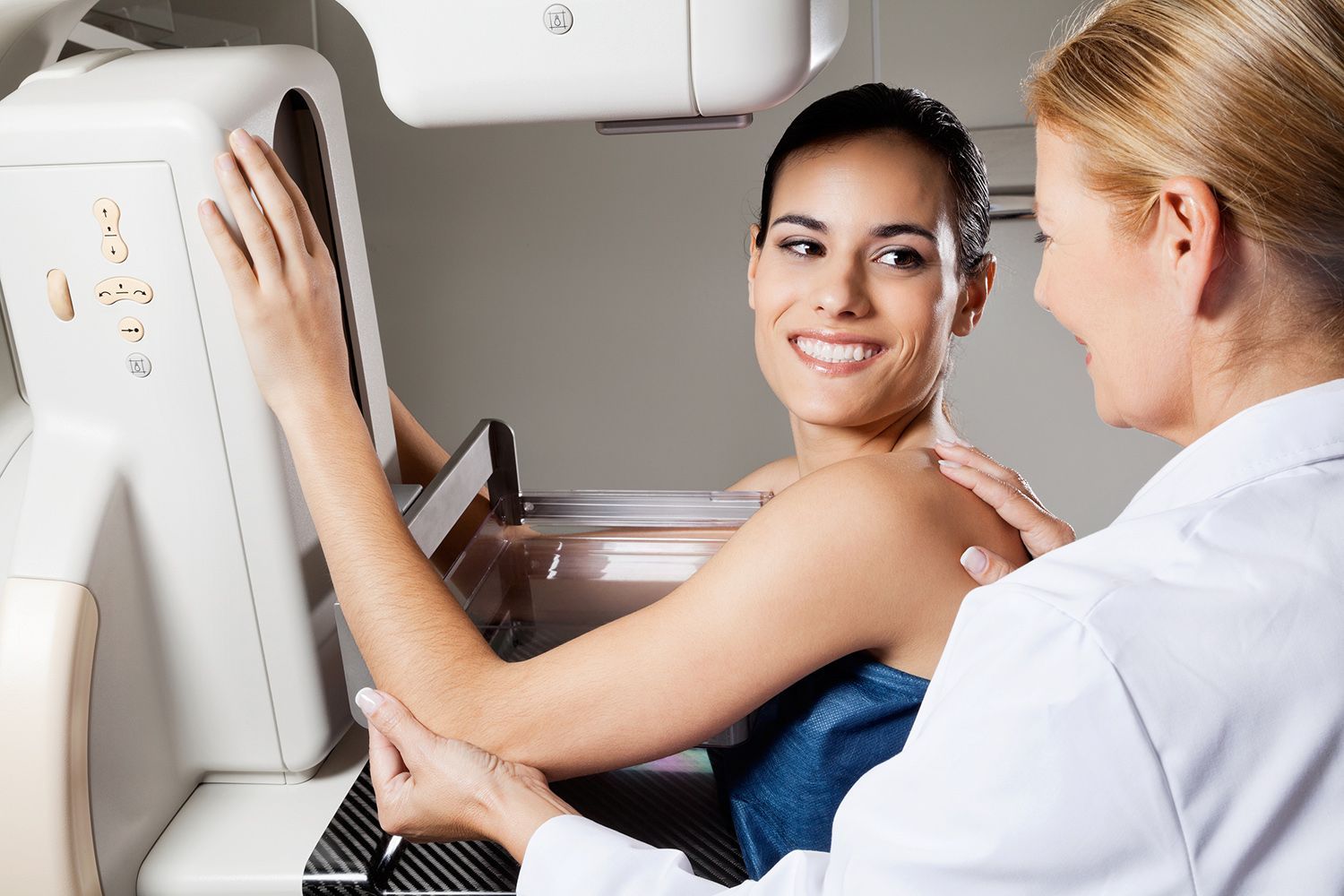
Mammography uses low-dose x-rays to examine the breast. Mammograms are important for early detection of breast cancers because they can show slight changes in the breast before a patient or healthcare provider can feel them. Mammograms are considered the most effective tool for early detection and diagnosis of breast cancers, which medical experts agree is essential for successful treatment.
MAMMOGRAPHY
MRI or Magnetic resonance imaging is a non-invasive imaging tool that uses strong magnet and radio waves to produce detailed diagnostic images of your internal organs and tissues. MRI uses highly sensitive techniques offering high quality diagnostic images that are not seen on traditional imaging methods.
MRI
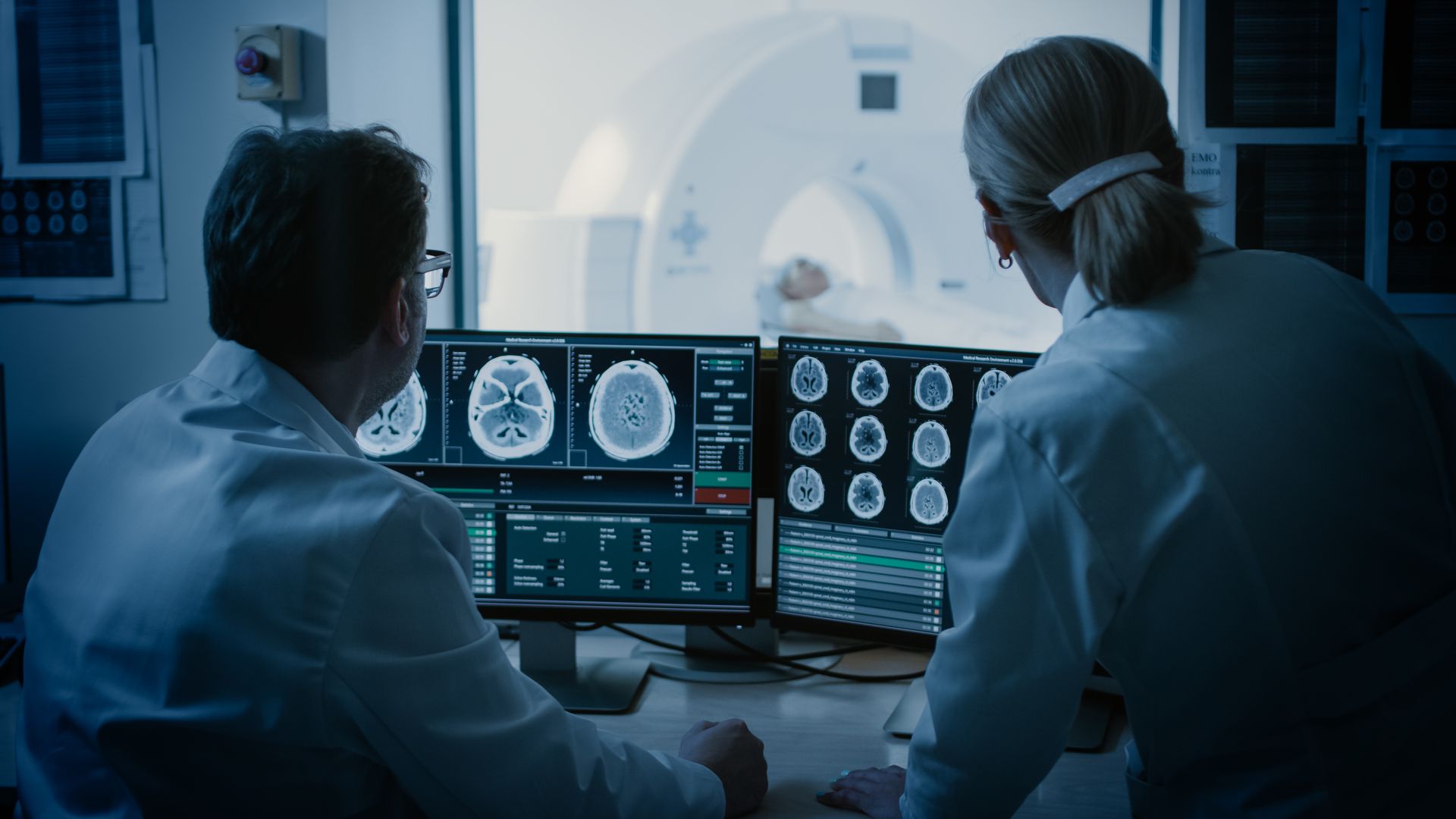
It is a medical test that helps identify the cause of an abnormal lump or mass in your body. This procedure is performed in the Radiology Department by a specially trained doctor called an interventional radiologist. A small needle is inserted into the abnormal area and a sample of tissue is removed, which is then given to a pathologist to examine under a microscope. The pathologist can determine if the abnormal tissue is cancer, non-cancerous tumor, infection or scar.
needle biopsy
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a method for visualizing soft tissue structures in the body. Images are generated by MRI scanners using magnetic fields instead of x-rays or other forms of radiation.
When applied to imaging of the prostate, MRI offers advantages in identifying potentially significant aggressive prostate cancers and recent advances in technology also facilitate direct lesion targeted biopsy
PROSTATE MRI
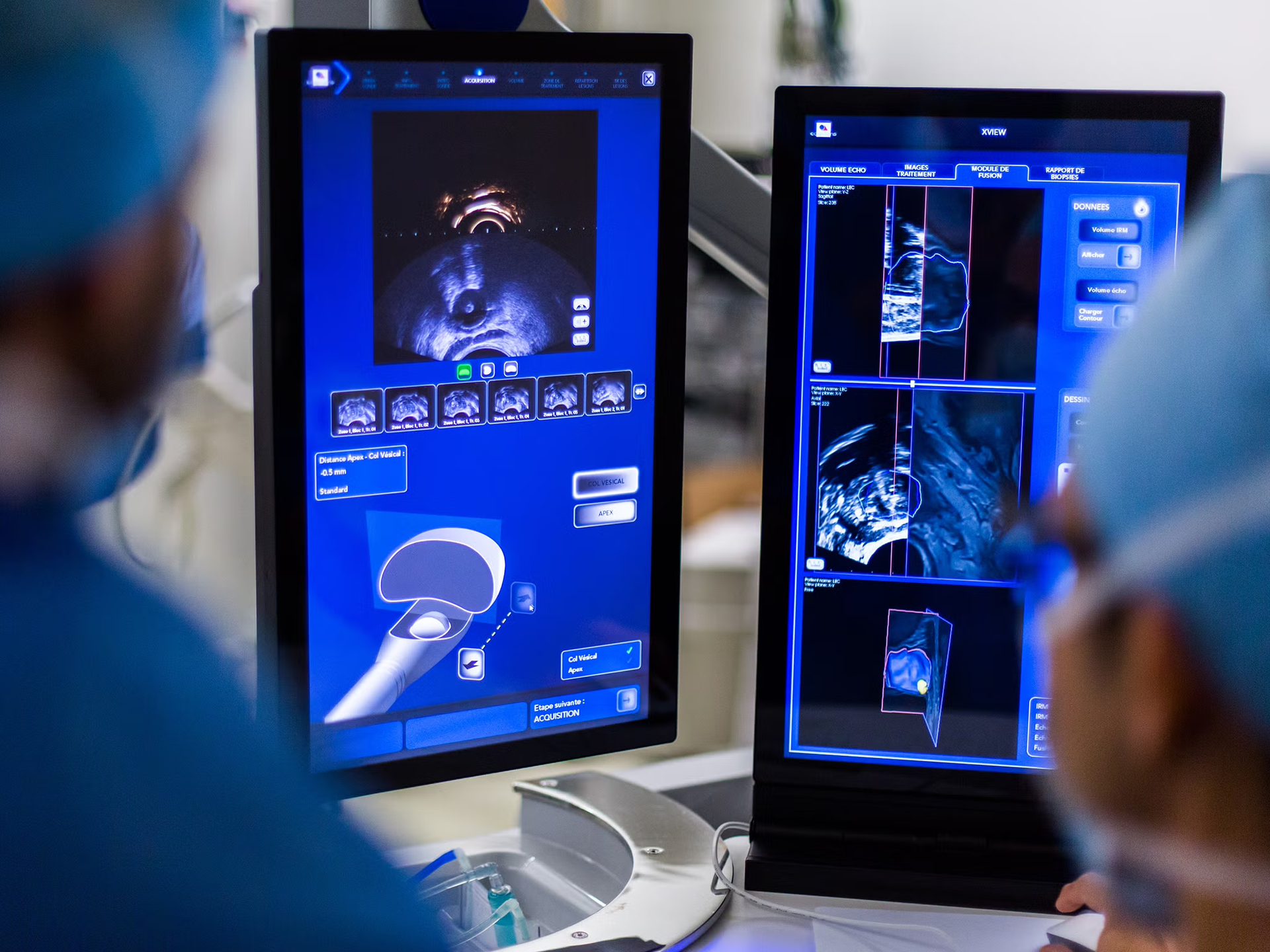
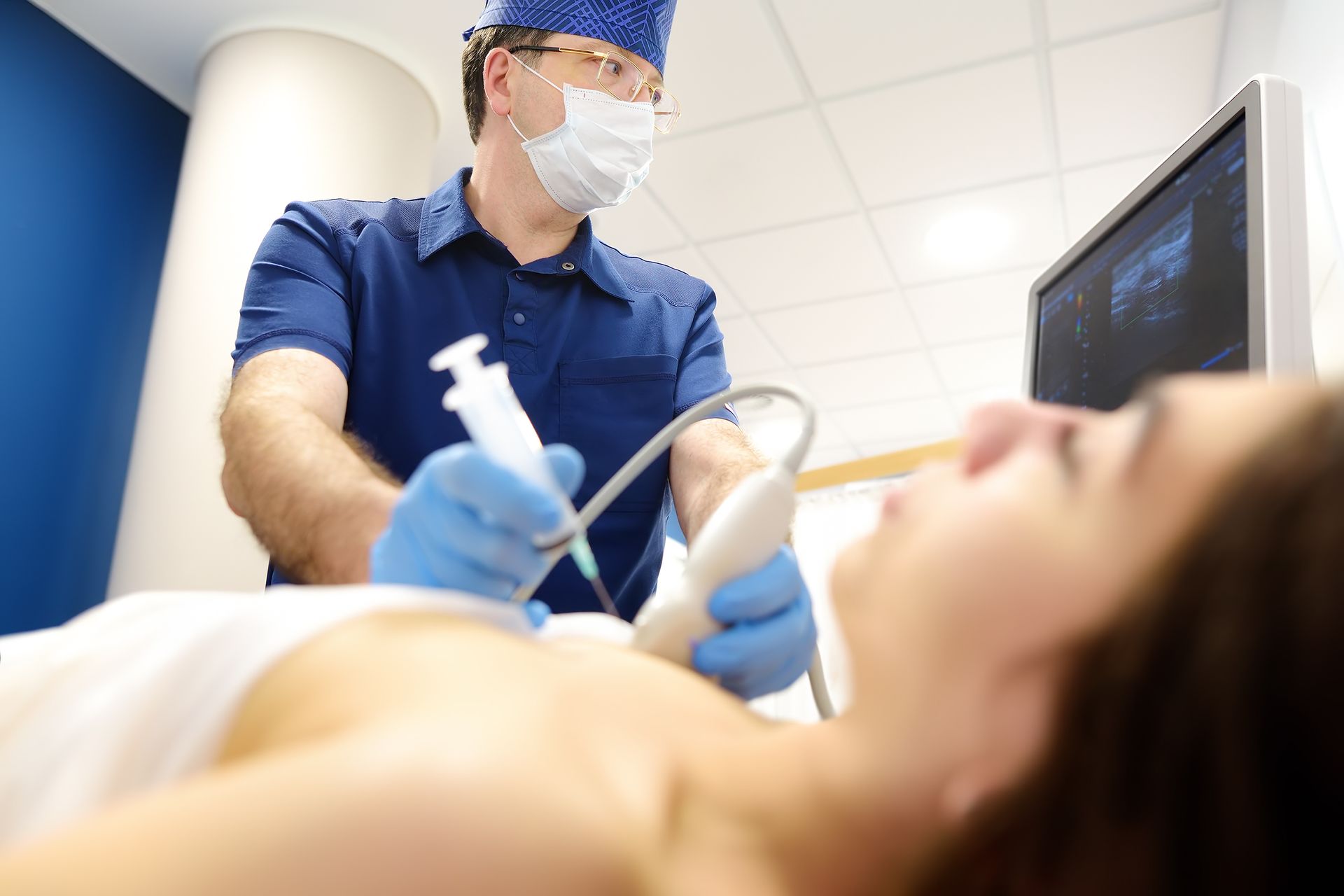
Many diseases involve the prostate gland. Ultrasound images are used in conjunction with a physical examination to localize and identify these disease processes. Diagnosis often requires obtaining a biopsy of a specific area. If a biopsy is needed, ultrasound can guide the biopsy needle into the lesion.
PROSTATE ULTRASOUND
Stereotactic breast biopsy was developed as an alternative to surgical biopsy. It is a less invasive way to obtain the tissue samples needed for diagnosis. This procedure requires less recovery time than does a surgical biopsy, and there is no significant scarring to the breast.
Your doctor, the radiologist and you may consider this type of biopsy when there is an abnormality found on a mammogram that cannot be felt. The radiologist can make a judgment about whether the procedure is technically feasible and your doctor may recommend it in your particular situation.
STEREOTACTIC BREAST BIOPSY

Ultrasound is an exam that uses sound waves to produce images. These images are obtained with a small ultrasound transducer (probe) that passes over the patient sending and receiving sound waves. Ultrasound does not use radiation to produce images and is a very safe procedure.
ULTRASOUND
An x-ray is a non-invasive procedure that uses small doses of radiation to produce digital images of the body. X-rays are traditionally the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging.
WHAT IS an X-ray?